Azure Service Connector lets you connect Azure compute services to backend services like Neon. It achieves this primarily by managing connection secrets (like database credentials using Azure Key Vault for secure storage) and configuring your application with the necessary connection details, typically via environment variables. Your application code then uses this injected configuration with standard database drivers and libraries to connect to Neon.
While Service Connector offers significant automation for some Azure-native services (like using Managed Identities), its integration with Neon currently relies on connection string authentication. This means you'll need to provide your Neon database credentials during setup, but Service Connector helps manage how these credentials are stored and exposed to your application.
This guide demonstrates connecting an Azure compute service (using Azure App Service as an example) to your Neon database using the Azure Service Connector via the Azure Portal.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- An Azure compute service to connect to Neon. Azure Service Connector supports the following compute services:
- Azure App Service
- Azure Functions
- Azure Container Apps
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Azure Spring Apps
- An existing Neon project created on Azure. If you don't have one, see Get started with Neon Serverless Postgres on Azure.
- Your Neon project's connection details readily available:
- Hostname (endpoint ID): e.g.,
ep-abc-123.eastus2.azure.neon.tech - Database name: e.g.,
neondb - Role (username): e.g.,
neondb_owner - Password
- You can find these in the Connection to your database widget on Neon Console. See Connect from any application.
- Hostname (endpoint ID): e.g.,
Supported authentication for Neon
Currently, Azure Service Connector supports connecting to Neon only via connection string.
- You will provide your Neon database hostname, database name, username, and password during the Service Connector setup.
- Managed Identity and Service Principal authentication methods, which provide passwordless connections and automated credential rotation for some Azure services, are not currently supported when connecting to Neon via Service Connector.
Connecting via the Azure portal
Follow these steps to create a service connection from your Azure compute service (e.g., App Service) to Neon.
-
Navigate to your Azure compute service: In the Azure portal, locate and select the specific App Service, Function App, or other compute resource you want to connect to Neon.
-
Open service connector: In the service's left-hand menu, scroll down to the Settings section and select Service Connector.
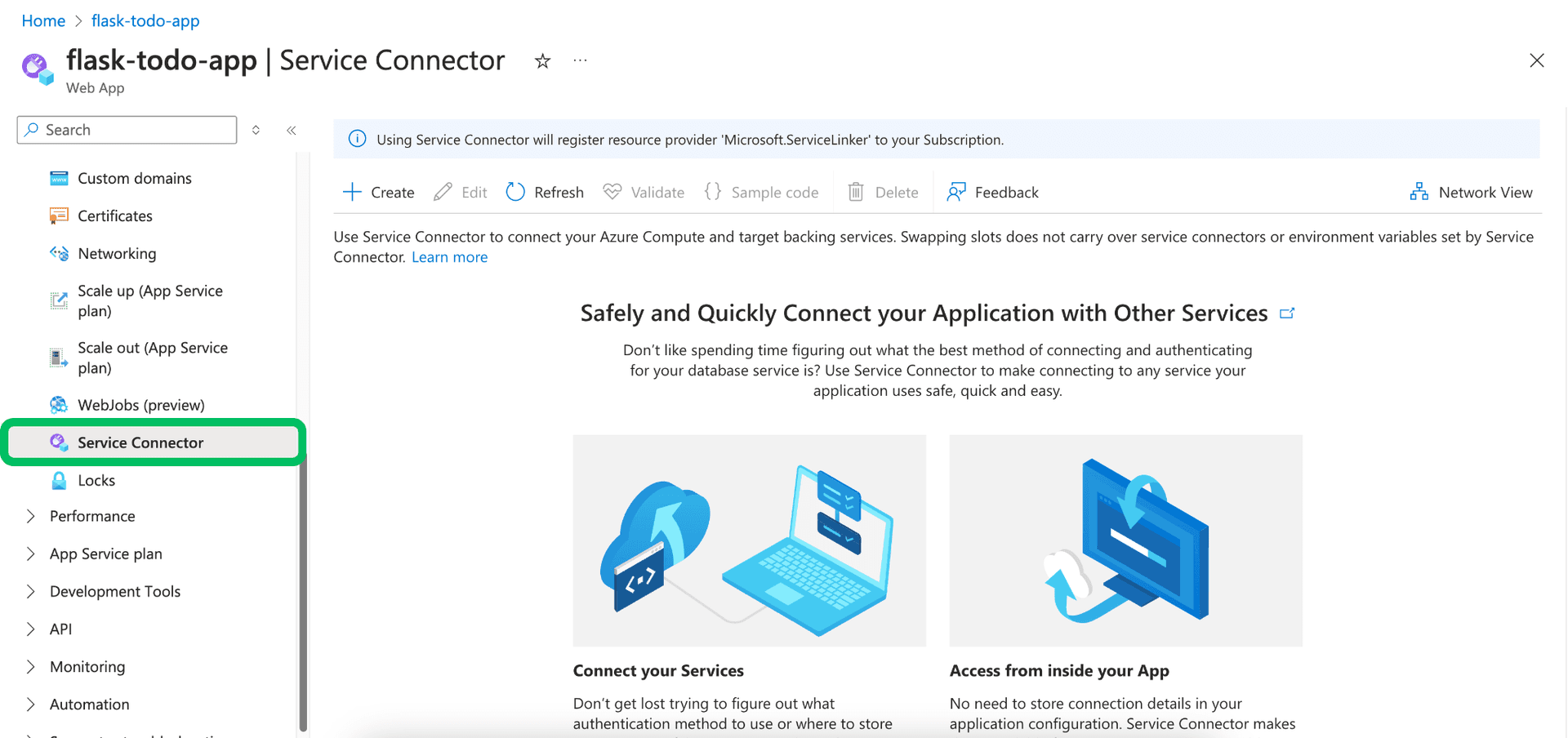
-
Start connection creation: Click the + Create button on the Service Connector page.
-
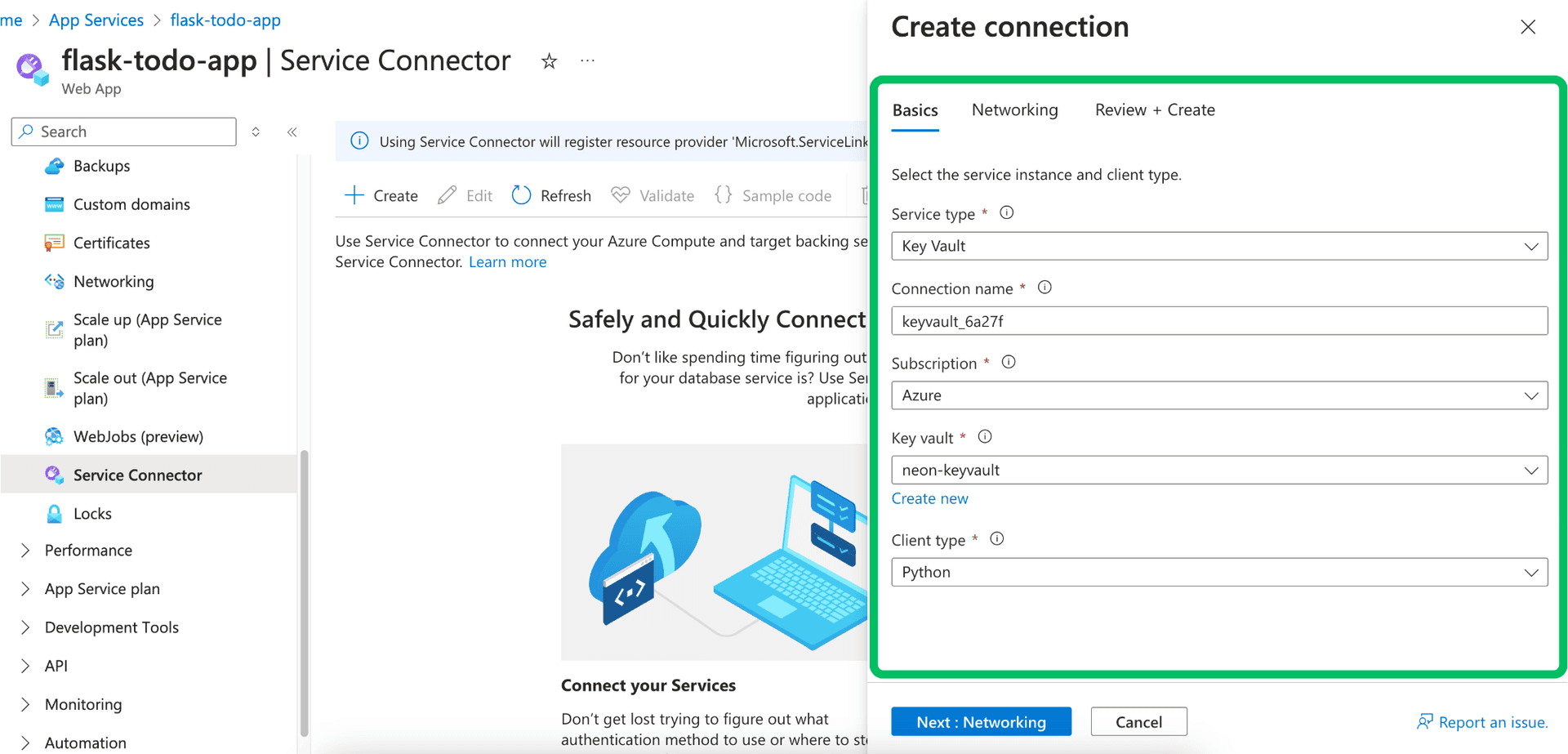
Configure basics:
-
Service type: Search for and select
Neon Serverless Postgres.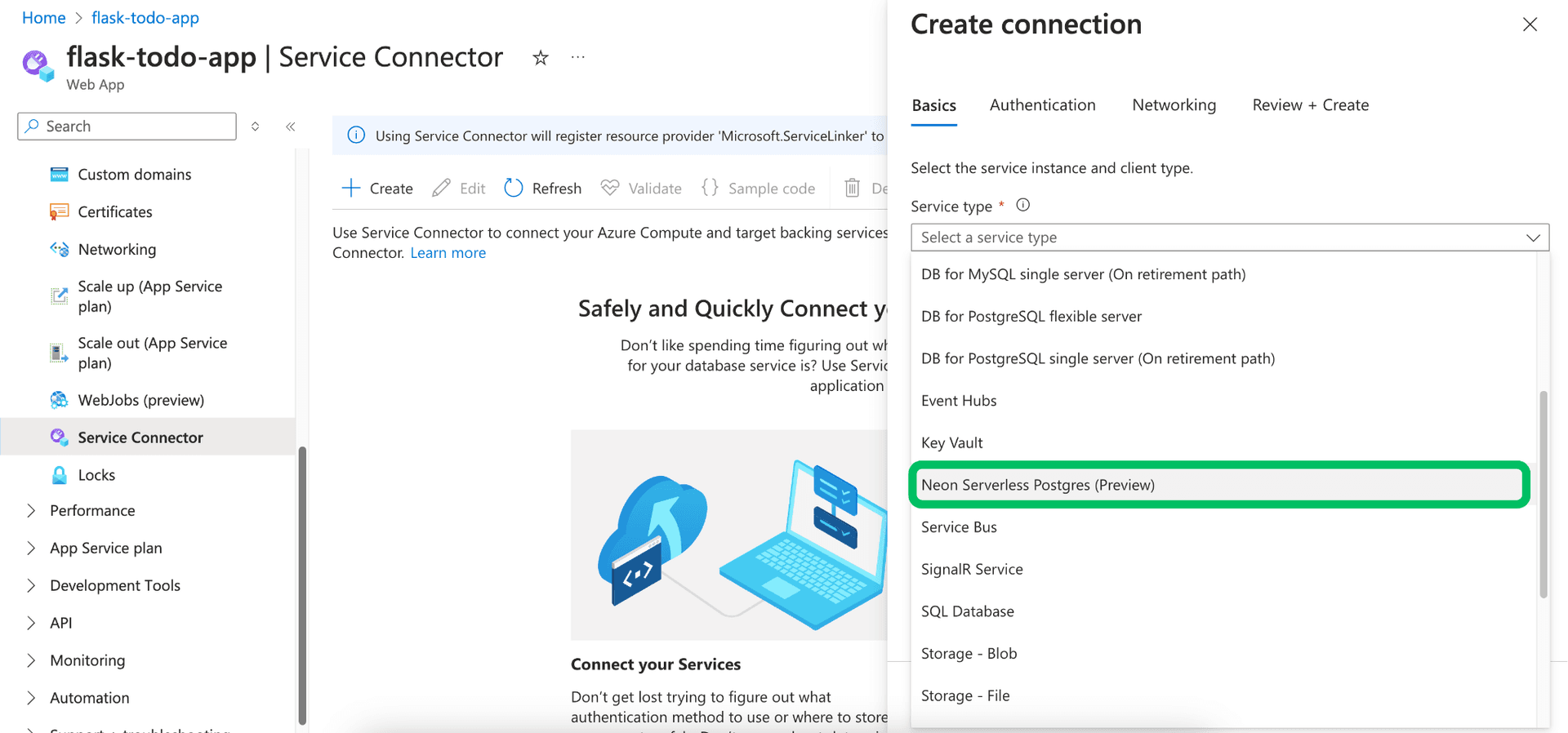
-
Connection name: Assign a descriptive name for this connection within Azure (e.g.,
neon_db_connection), or accept the auto-generated name. This name is for Azure management purposes. -
Neon Postgres hostname: Manually enter the full hostname (including the endpoint ID) from your Neon project's connection details. (Service Connector currently cannot automatically discover existing Neon resources).
-
Neon Postgres database name: Manually enter the name of the Neon database you wish to connect to. (e.g.,
neondb). -
Client type: Select the primary programming language or framework your application uses (e.g.,
.NET,Python,Java,Node.js,Go, etc.). This choice influences the naming convention and format of the environment variables Service Connector creates. -
Click Next: Authentication.
-
-
Configure authentication:
-
The Connection string option will be pre-selected, as it's the only supported method for Neon.
-
You now need to provide your Neon Username and Password. Service Connector offers two ways to handle the password:
-
Database credentials:
You can use database credentials for the first time connection to create a new Key Vault secret. For applications that already have a Key Vault secret, you can use the Key Vault option to reference the existing secret.
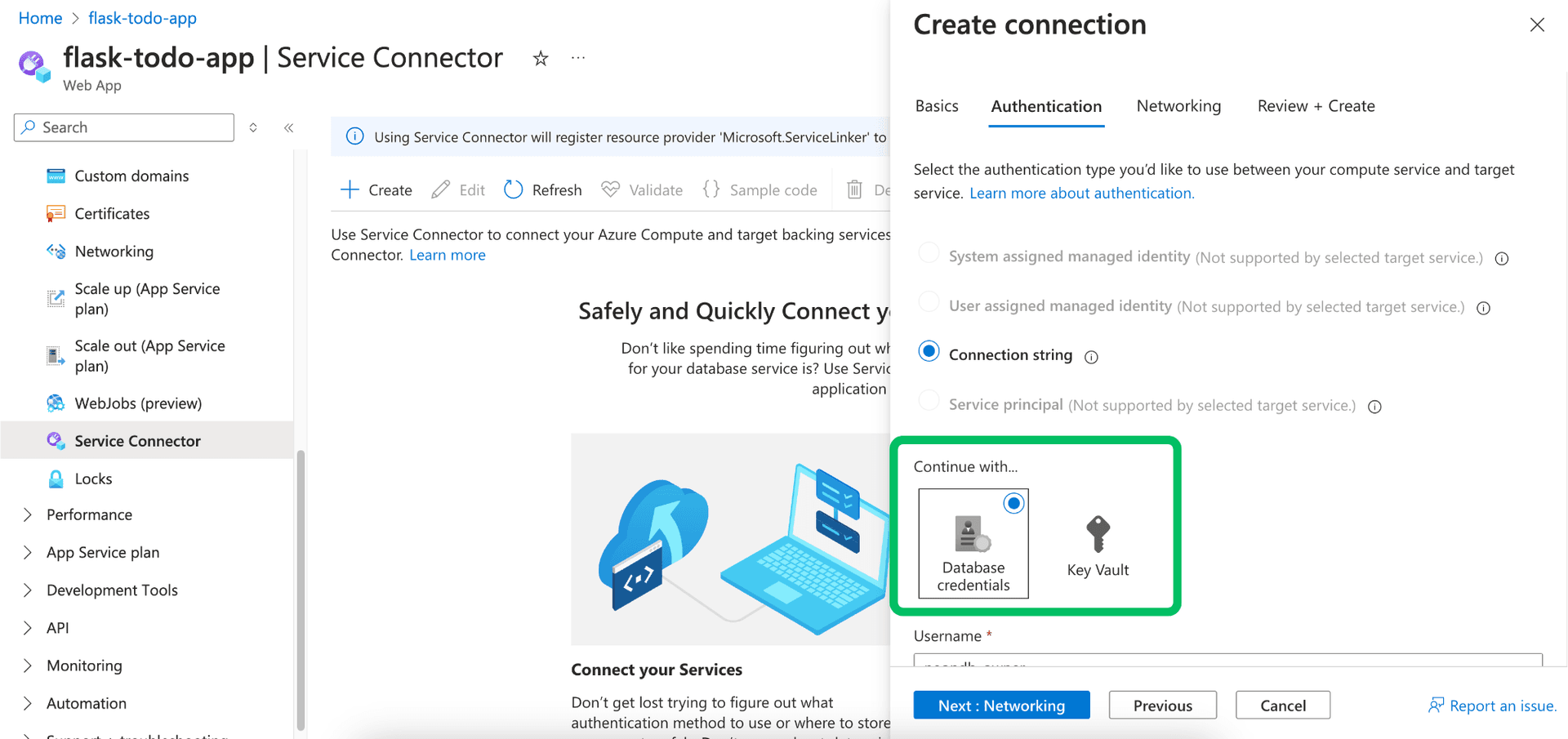
- Select the Database credentials tile.
- Enter your Neon database Username.
- Enter your Neon database Password.
Important
Check the Store Secret in Key Vault box. This prompts you to select an existing Azure Key Vault or Create new.
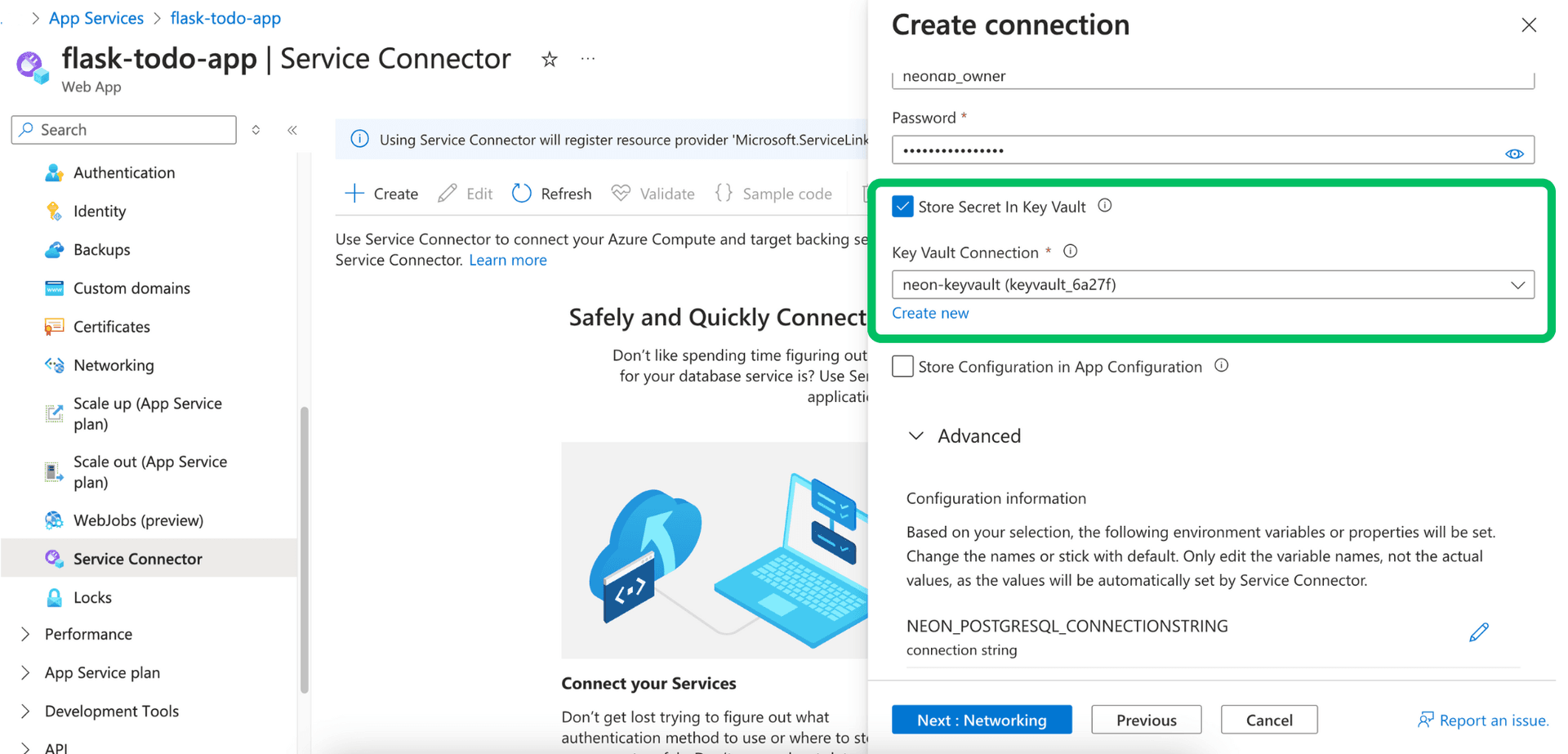
If you create new, Azure provisions a Key Vault instance and securely stores the password as a secret within it.
Service Connector will then reference this secret. This is more secure than storing the password directly in App Service configuration.
-
Key Vault reference (for pre-existing Key Vault secret):
- Select the Key Vault tile.
- Choose the Subscription and Key vault containing your pre-existing secret.
- Select the Secret that holds your Neon database password.
- Enter your Neon database Username manually in the provided field.
-
-
Review the Configuration information section. This previews the environment variables Service Connector will set based on your choices (e.g.,
NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRINGor individual components).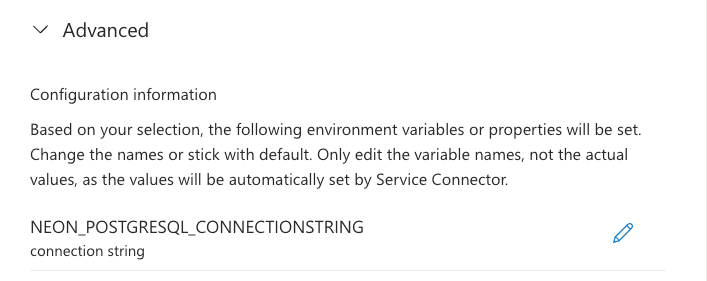
If your application uses a custom naming convention for environment variables that differs from the default ones provided by Service Connector, you can choose to modify the variable names accordingly by clicking the Edit icon next to the variable name.
-
Click Next: Networking.
-
-
Configure networking:
- For Neon connections via Service Connector in the portal, you can skip this step. Network access controls (like IP allow lists) are managed directly within your Neon project settings, not through Service Connector's network configuration options (Firewall, Service Endpoint, Private Endpoint) which apply primarily to Azure target services.
- Refer to Neon's IP Allow documentation to configure network access if needed.
- Click Next: Review + Create.
-
Review and create:
- Review the summary of the connection details. Verify the target service (Neon), compute service, authentication method, and especially the environment variables that will be created.
- Click Create.
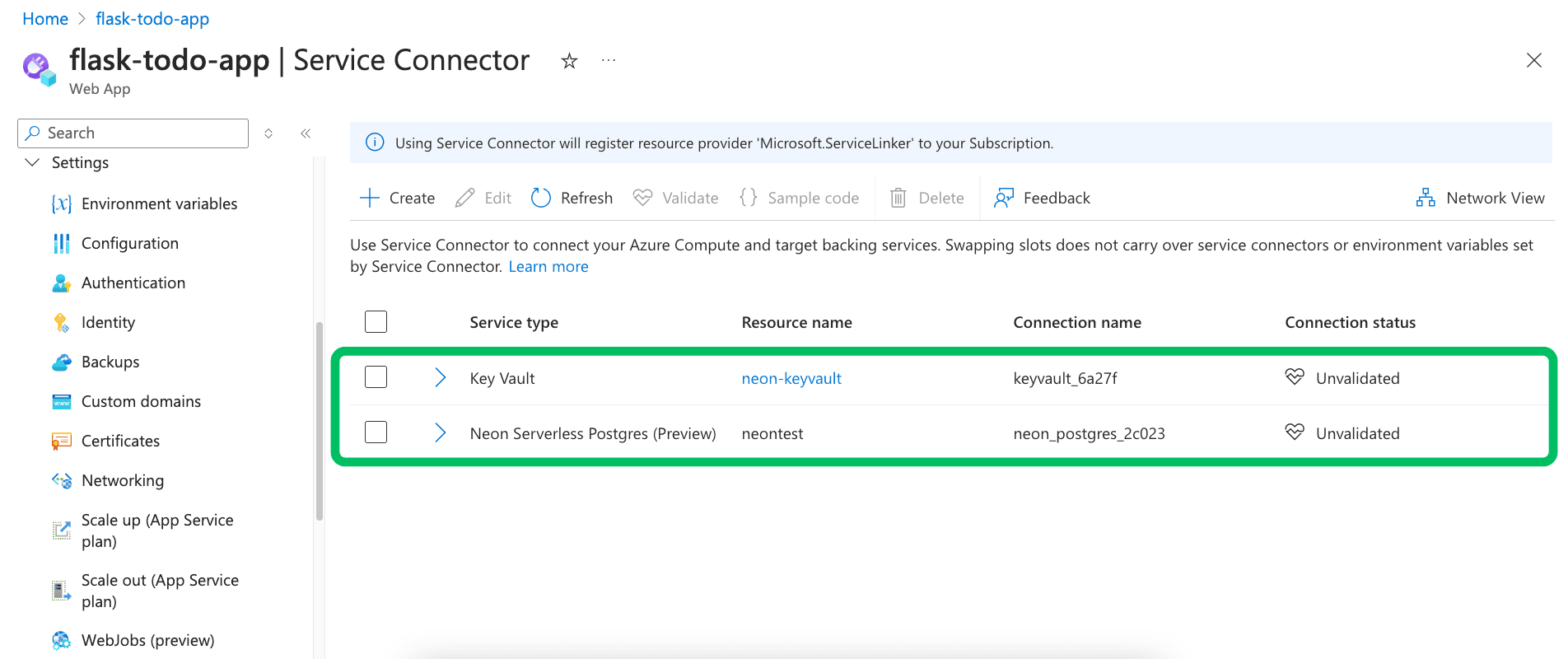
Azure will now provision the connection. This process might take a minute or two. Service Connector configures the necessary settings on your Azure compute service (primarily environment variables, potentially linking to Key Vault).
You can confirm the connection was created successfully by returning to the Service Connector page for your compute service. The new Neon connection should be listed.
Using the connection in your application
After successful creation, Service Connector injects the connection details into your Azure compute service's environment. Your application code accesses these environment variables to connect to Neon using a standard PostgreSQL driver or library appropriate for your chosen language/framework.
How Service Connector exposes the details depends on the Client type you selected:
- For most client types (.NET, Python, Go, Java, PHP, Ruby): Service Connector creates a single environment variable named
NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRINGcontaining the full, formatted connection string. - For other client types (like Node.js, Django or other): Service Connector creates individual environment variables like
NEON_POSTGRESQL_HOST,NEON_POSTGRESQL_PORT,NEON_POSTGRESQL_DATABASE,NEON_POSTGRESQL_USER, andNEON_POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD.
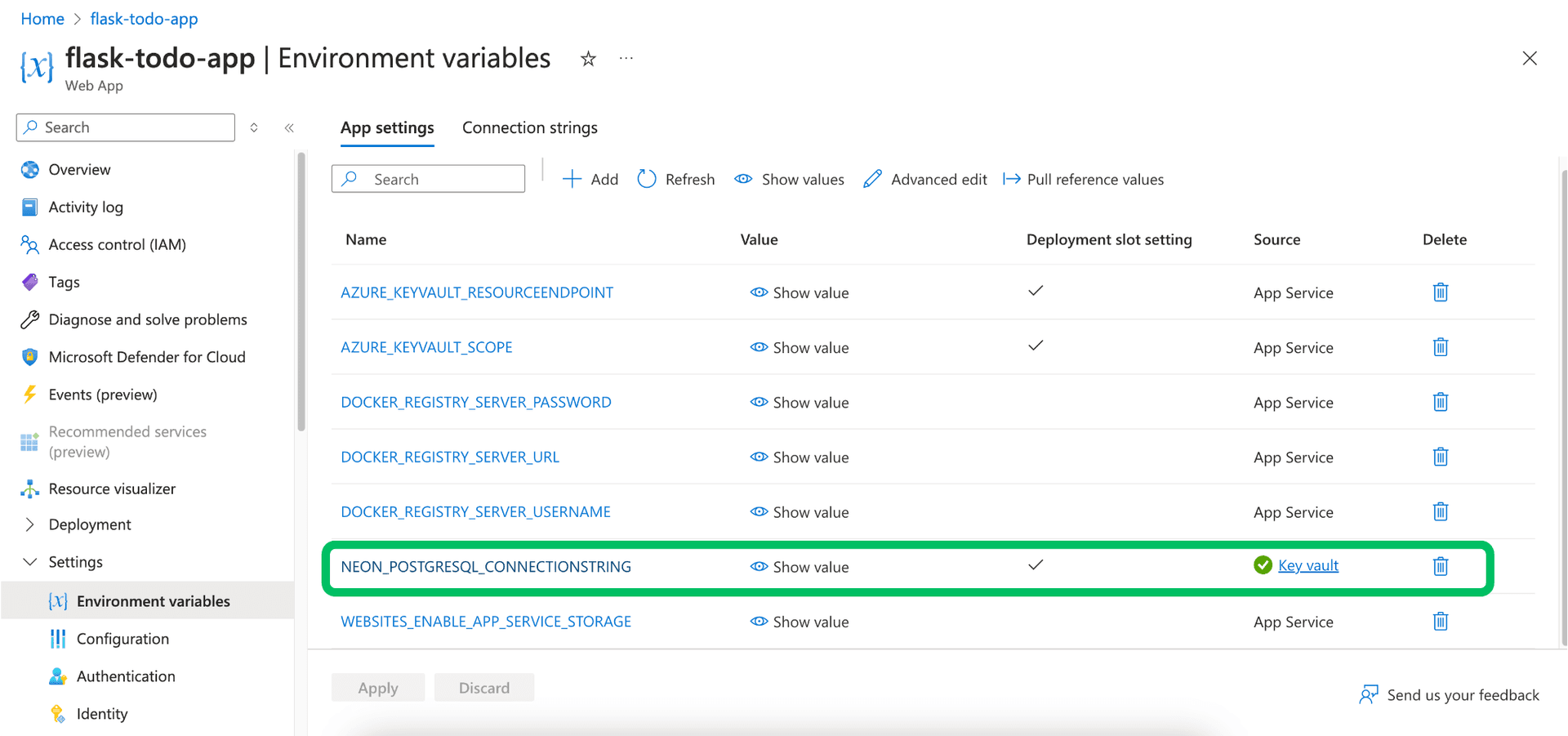
You can view the configured environment variables in your App Service under Settings -> Environment variables.
Here's an example of how to use the connection string in a Python application using the psycopg2 library:
import os
import psycopg2
connection_string = os.environ.get("NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRING")
if not connection_string:
print("Error: NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRING environment variable not set.")
# Handle error appropriately - raise exception, exit, etc.
else:
conn = None
try:
conn = psycopg2.connect(connection_string)
print("Successfully connected to Neon!")
with conn.cursor() as cur:
cur.execute("SELECT version()")
print(f"PostgreSQL version: {cur.fetchone()[0]}")
except (Exception, psycopg2.DatabaseError) as error:
print(f"Error connecting to Neon: {error}")
finally:
if conn is not None:
conn.close()
print("Database connection closed.")Adapt the code to fetch and use the environment variables according to your application's language, framework, and the specific variables created by Service Connector based on your "Client type" selection. Refer to the table below or the Azure documentation for specific variable names.
Environment variables and properties by client type
| Client type | Primary configuration | Example variable / property | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| .NET | Env var: connection string | NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRING | Standard Npgsql format. (eg, Server=ep-still-mud-a12aa123.eastus2.azure.neon.tech;Database=<database-name>;Port=5432;Ssl Mode=Require;User Id=<username>). |
| Java (JDBC) | Env var: connection string | NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRING | jdbc:postgresql://... format. |
| Java (Spring Boot JDBC) | Application Properties | spring.datasource.url, ...username, ...password | Service Connector sets corresponding env vars that Spring Boot picks up. |
| Python (psycopg2) | Env var: connection string | NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRING | Key-value format dbname=... host=... user=... password=... port=... sslmode=require |
| Go (pg) | Env var: connection string | NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRING | Similar key-value format as Python. |
| Node.js (pg) | Env Vars: Individual Components | NEON_POSTGRESQL_HOST, NEON_POSTGRESQL_USER, NEON_POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD, NEON_POSTGRESQL_DATABASE, NEON_POSTGRESQL_PORT, NEON_POSTGRESQL_SSL | Construct connection object/string from parts. |
| PHP | Env var: connection string | NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRING | Key-value format. |
| Ruby | Env var: connection string | NEON_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTIONSTRING | Key-value format. |
| Django | Env vars: individual components | NEON_POSTGRESQL_NAME, NEON_POSTGRESQL_HOST, NEON_POSTGRESQL_USER, NEON_POSTGRESQL_PASSWORD | Construct Django database settings from parts. |
Resources
- Neon on Azure
- Official Azure Service Connector Documentation
- Azure Docs: Integrate Neon Serverless Postgres with Service Connector
- Neon Documentation
- Find your Neon connection details
- Neon IP Allowlisting
Need help?
Join our Discord Server to ask questions or see what others are doing with Neon. Users on paid plans can open a support ticket from the console. For more details, see Getting Support.